How To Use Etc Resolv Conf
Echo e main ndns none etc networkmanager conf d no dns.
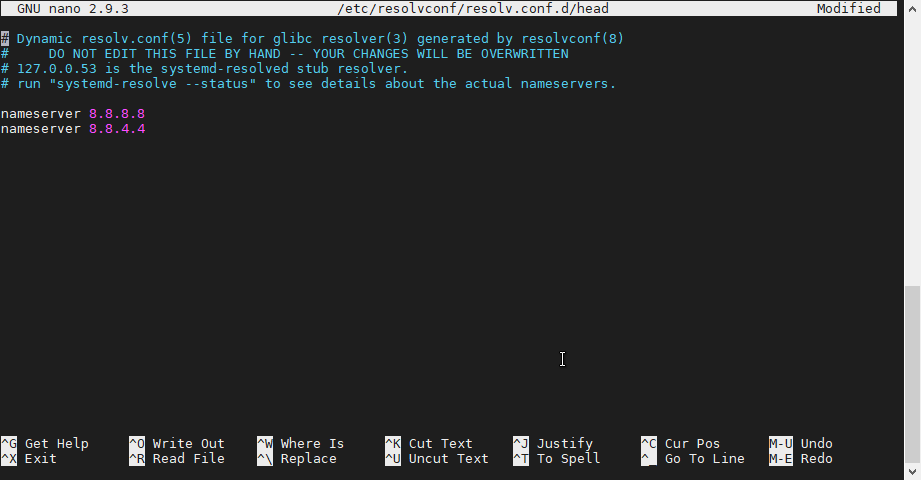
How to use etc resolv conf. The etc resolv conf is resolver configuration file for linux and unix like operating systems. Etc resolv conf can have one or more name server entries. In ubuntu 20 04 the default nameserver is 127 0 0 53. Create a file such as etc resolv conf manually configured and add the dns configuration for your environment to it. Set the dns option in the main configuration section to none to disable dns handling in networkmanager.
Remove the etc resolv conf file. So instead of having to manually overwrite create configuration files in etc you can simply re link etc resolv conf to point to the run systemd resolve resolv conf file and all should be just fine. When using dhcp dhclient usually rewrites resolv conf with information received from the dhcp server. In addition to listing resolving servers the resolv conf file can also take the search option that will save you a great deal of typing in the right. Use the same parameters and syntax as in the original etc resolv conf.
The file etc resolv conf is a file containing the dns resolver or ip address of the dns server nameserver which functions to translate from domain names to ip addresses. The etc resolv conf configuration file contains information that allows a computer to convert alpha numeric domain names into the numeric ip addresses. The below commands sets this option in a new conf d no dns conf configuration file restarts the networkmanager service and deletes the networkmanager generated resolv conf file. The process of converting domain names to ip addresses is called resolving. If one name server is not working then the server will attempt to use another one.
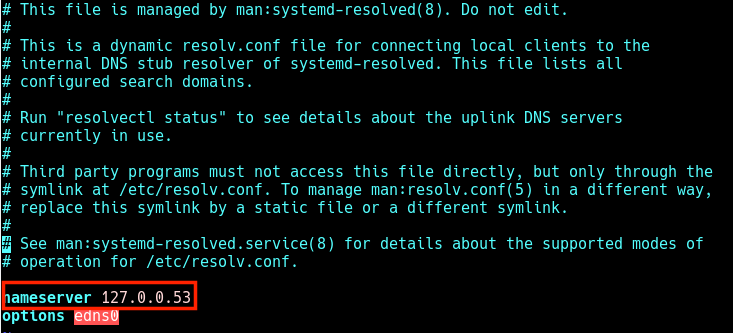
It contains the resolvers that the system will query in order to convert hostnames to ip addresses and vice versa. The etc resolv conf file configures how the linux system resolves hostnames. Sudo ln sf run systemd resolve resolv conf etc resolv conf you should now be able to edit the settings even from the network manager in gnome.